Understanding Autoimmune Diseases and NAD+
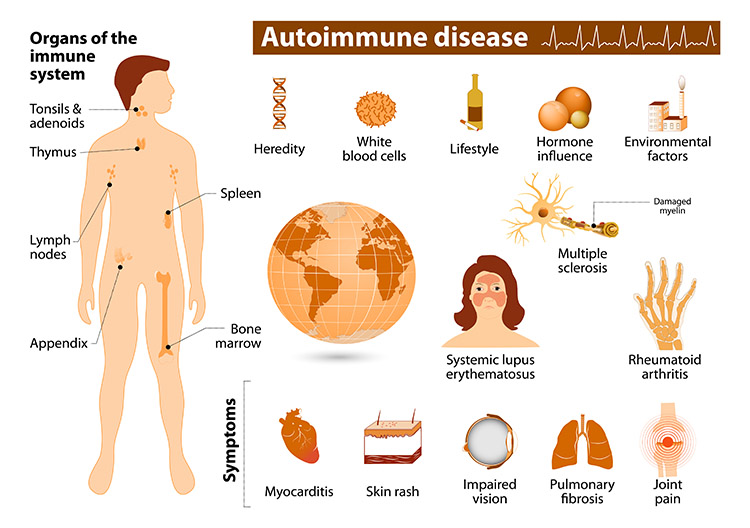
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the immune system erroneously attacks the body’s own cells, mistaking them for harmful invaders. Typically, the immune system defends the body against pathogens like bacteria and viruses by producing antibodies that neutralize these foreign agents. However, in autoimmune diseases, the immune system fails to distinguish between self and non-self, leading to attacks on various tissues and organs.
Types of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases can target specific organs or affect the entire body. Some common autoimmune diseases include:
- Type 1 Diabetes: The immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): The immune system attacks the myelin sheath, the protective covering of nerve cells, causing symptoms like numbness, poor coordination, and mobility issues.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: The immune system targets the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and joint damage.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): This includes Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, and ulcerative colitis, which affects the colon and rectum.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus): The immune system attacks various body parts, including the kidneys, joints, brain, and heart.
- Pernicious Anemia: The immune system attacks stomach cells responsible for producing intrinsic factor, essential for vitamin B12 absorption.
- Celiac Disease: The immune system reacts to gluten, damaging the small intestine.
- Psoriasis: Rapid skin cell production leads to thick, scaly patches on the skin, which can be painful and prone to bleeding.
Rising Prevalence and Causes
The incidence of autoimmune diseases is increasing worldwide. In the Asia, their prevalence has risen by 50% over the past 25 years. The exact causes remain unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of autoimmune diseases increases risk.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals and a Western diet may trigger autoimmune responses.
- Hygiene Hypothesis: Reduced exposure to pathogens due to improved hygiene standards may cause the immune system to overreact to harmless substances.
Treatment Approaches
Current treatments for autoimmune diseases focus on moderating the immune response and managing symptoms. Despite advancements, scientists continue to explore more effective treatments to address the underlying causes of these diseases.
NAD+ and Autoimmune Diseases
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is a vital biochemical compound present in all cells, essential for energy production and cellular health. Emerging research suggests NAD+ may play a significant role in regulating immune responses and could be a potential treatment for autoimmune diseases.
Benefits of NAD+ IV Therapy
NAD+ has been found to offer numerous health benefits:
- Neurological Health: Maintains healthy nerve function.
- Muscle Maintenance: Helps preserve muscle mass and strength.
- Cardiovascular Protection: Supports heart health.
- Anti-Aging: Slows down the aging process.
- Stress Resistance: Protects against stress effects.
- Immune Function: Enhances the immune system’s ability to combat diseases.
NAD+ levels naturally decline with age and are often lower in individuals with various health conditions. Increasing NAD+ levels through intravenous (IV) therapy can help reverse these declines and potentially improve health outcomes.
Research Evidence
- Diabetes: Diabetics typically have lower NAD+ levels, leading to increased oxidative stress and complications. Studies have shown that IV administration of NAD+ can improve health outcomes by reducing oxidative stress and associated complications.
- Multiple Sclerosis: In MS, the immune system attacks the myelin sheath of nerve cells. Research indicates that NAD+ can help restore immune balance and repair myelin damage, encouraging the development of NAD-based therapies for MS.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Reduced NAD+ levels lead to the erosion of the intestinal lining and inflammation. Increasing NAD+ levels has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve intestinal health.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current treatments focus on symptom relief rather than addressing the autoimmune response. NAD+ therapy offers a potential long-term solution by directly influencing NAD+ metabolism, a crucial factor in the disease’s development.
- Psoriasis: NAD+ components like nicotinamide can reduce excessive skin cell production, thereby improving the condition of psoriasis.
Administration Methods
NAD+ can be administered orally or intravenously. However, oral administration is less effective due to partial absorption in the digestive tract. IV administration ensures that NAD+ directly enters the bloodstream, providing more efficient and effective results.
Conclusion
The increasing prevalence of autoimmune diseases underscores the need for innovative treatments like NAD+ IV therapy. While current research is promising, ongoing studies continue to explore the full potential and mechanisms of NAD+ in treating autoimmune conditions. Patients interested in NAD+ IV therapy should consult with our healthcare provider in Kuala Lumpur and Penang to ensure its safety and suitability for their specific condition.
References
- 2023: The potential of CD38 protein as a target for autoimmune diseases.
- 2022: The CD38 glycohydrolase and the NAD sink: implications for pathological conditions.
- 2022: Boosting NAD+ blunts TLR4-induced type I IFN in control and systemic lupus erythematosus monocytes.
- 2022: A purine metabolic checkpoint that prevents autoimmunity and autoinflammation.
- 2022: Antioxidative enzyme NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) modulates the differentiation of Th17 cells by regulating ROS levels.
- 2022: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism in the immune response, autoimmunity, and inflammageing.
- 2022: NAD(+) metabolism drives astrocyte proinflammatory reprogramming in central nervous system autoimmunity.
- 2021: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide treatment alleviates the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by activating autophagy and inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome.
- 2021: NAD+ improved experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by regulating SIRT1 to inhibit the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.




