NAD+ Therapy: Discover the Power of Cellular Rejuvenation.
One of Life’s Essentials
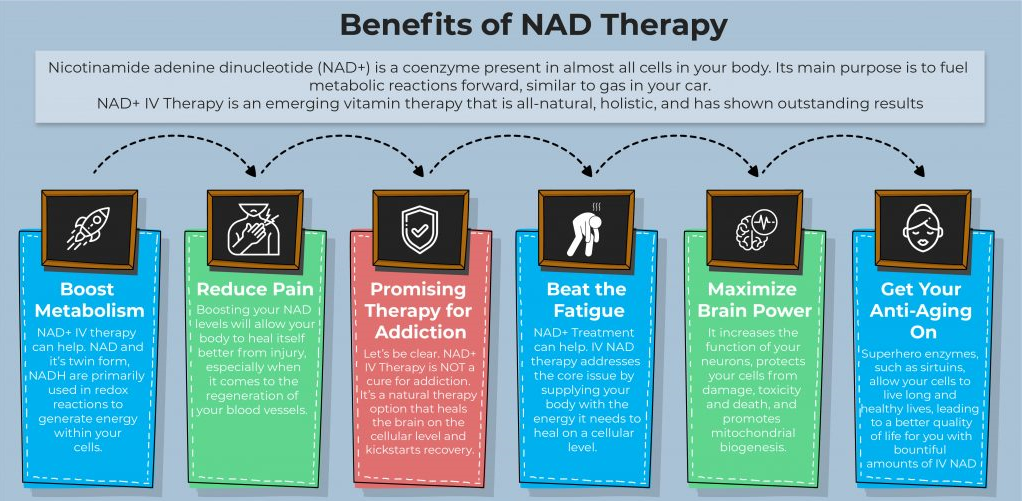
NAD+, also known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a naturally occurring coenzyme that supports several body functions. It controls circadian rhythms, promotes metabolism, disarms free radicals, and, most significantly, makes it possible for mitochondria to turn food into energy. Unfortunately, as we age, NAD+ production decreases, leaving us with less energy, more ageing symptoms, and an increased risk of sickness. However, keeping NAD+ levels high can aid in preventing these problems, and we are pleased to offer NAD+ IV therapy in all of our centres. The following are some of the advantages of NAD+ IV therapy:
- Increased energy: As was already noted, NAD+ is essential for the mitochondria’s ability to produce energy. NAD+ IV treatment increases NAD+ levels, which boosts energy and fights weariness.
- NAD+ is thought to defend against DNA damage and aid in cell repair, which might lessen ageing symptoms like fine lines and wrinkles.
- Enhancement of brain function and improvement of cognitive capacities have been linked to NAD+ IV treatment.
- Recovery from addiction: NAD+ has been demonstrated to lessen drug cravings and lessen withdrawal symptoms, making it a possible therapy for this condition.
- NAD+ has been proven to potentially prevent or slow down neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s because of its neuroprotective characteristics.
- Cardiovascular Health: NAD+ has been demonstrated to contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular disease by enhancing endothelial function, or the wellbeing of the cells that line blood arteries. Atherosclerosis, a disorder in which plaques accumulate in the arteries and cause restricted blood flow and an elevated risk of heart attack and stroke, is largely caused by endothelial dysfunction. By encouraging the synthesis of nitric oxide, a chemical that helps relax blood arteries and enhances blood flow, NAD+ has been proven to improve endothelial function.
You may read the PubMed article on NAD+ here.